Kia ora!
I’m Chun Shen, a Research Fellow at the University of Otago, New Zealand. My research uses AI to study Hep B sequences, with a focus on how different genotypes produce spliced RNAs, molecules that play a role in viral replication and disease progression.
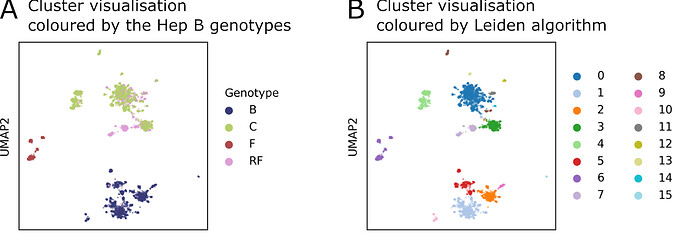
The figure below shows how AI can distinguish between HBV genotypes based on their ability to produce different spliced RNAs. In Panel A, the coloured clusters represent known genotypes: B (blue), C (green), F (red), and RF (pink). RF stands for “recombination forms” - viruses that have mixed genetic material from different genotypes. Interestingly, RF overlaps with genotype C in this view.
However, when we apply a clustering algorithm called Leiden (Panel B), the AI identifies 16 distinct groups, revealing more subtle differences in the data. This suggests that even within overlapping genotypes, there may be hidden diversity that could affect how the virus behaves or responds to treatment.
This work helps us better understand the complexity of Hep B and could eventually support more personalised approaches to managing the infection.
Let’s talk AI and Hep B.